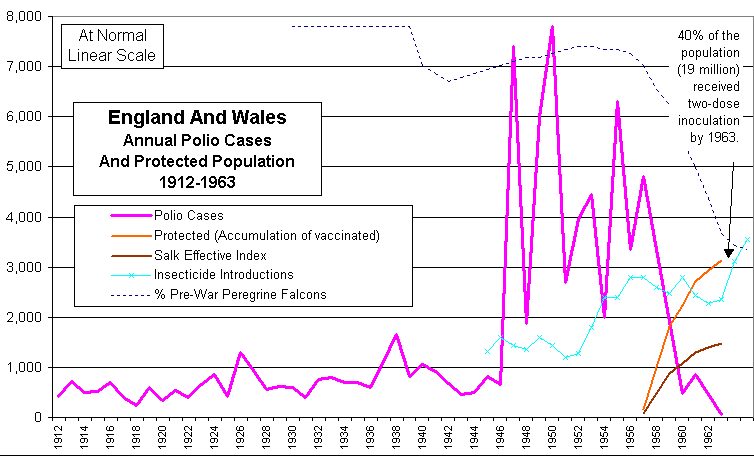
Britain, 1912 to 1963
Pesticides and Polio
Commentary by Jim West
Compare this with the U.S. experience (ref1 and ref2). It appears the fundamental disease, chemical, and political relationships are similar in both Britain and U.S.. Data seems to be more available for the U.S. Britain escaped the great polio epidemic of 1916, which was then severe in New York City, U.S. |
|
Comments |
|
| 1945 | DDT introduced in Europe, Britain, and US. |
| 1951 | DDT phase-out and awareness of hazards begins, probably in synch with US. |
| 1956 | Dieldrin, Aldrin were introduced 1956 in Britain, as in US. |
| 1956 | Pesticide laws (including labeling regulations) enacted in US. Assume same in Europe. |
| 1970 | DDT was banned in Europe/Britain in 1970, similar to US date. |
| Research by John Sheail concludes that persistent pesticide Dieldrin on seed dressings caused decline of bird populations in Britain. | |
| My view differs slightly: The introduction of massive quantities of organophosphate pesticides (replacing DDT, BHC, the previous pesticide generation) during the same era, mid-late 1950s, likely also contributed to bird decline, and may have been the primary cause of the avian decline. Increased public awareness and regulations would have contributed to the avian revival after 1962. | |
| England and Wales pesticide production data should be included, however, this is difficult to acquire, as it is probably not allowed in public domain. Can only assume laws and production data are same as in U.S., where pesticide production data cannot be disseminated under threat of imprisonment, however, rare data is provided, though only for US, at "Overview". | |
| Polio vaccine, 2 doses per person by 1963 | 19,000,000 of 46,973,000 population, means 40% of population received 2 doses of vaccine, by 1963. Polio vaccines went into effect 1957, in Britain, a year later than U.S. (U.S. first mass test was in 1954). |
| British pesticide reference | Pesticides and nature conservation: the British experience, 1950-1975, by John Sheail, Oxford: Clarendon Press; New York: Oxford Univ. Press, p231 |
| British polio references |
B.R. Mitchell, British Historical Statistics, 1988, Cambridge
University Press, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, New
Rochelle, Melbourne, Sydney Vaccine Innovation and Adoption: Polio
Vaccines in the UK, the Netherlands and West Germany, 1955–1965,
ULRIKE LINDNER, PhD and STUART S BLUME, Prof. Dr |
Interplay of Epidemic Factors
Pesticides are not the only epidemic factor. Epidemics consist of three main areas of injustice: pesticides,
vaccines, and industrial pollution, underwritten by biased diagnostics.
There are differences, in terms of metabolism modification, medical exploitation, industrial protection.
Epidemic Factors
Prioritized by Industrial Necessity
Priority
Factor
Primary Effect
Secondary Effect
Tertiary Effect
1
Pollution (air, water,
food)
Economic:
Required means of free waste disposal. Must be protected
from liabilities.
Requires masking by
propaganda and disinfo. The effects of pollution are dark
and would interfere with esprit de corp and tarnish the
image of the current style of technology.
Economic: Raises
social metabolism, thereby increases production, confusion,
dumbness, errors, disease, and the frequency of all interactions,
and importantly the frequency of financial transactions, creates market diversity of misinformed options.
http://harpub.tk/toxcredo.htm
2
Pesticides
Economic: Raises
social metabolism, thereby increases production, confusion,
dumbness, errors, disease, and the frequency of all interactions,
and importantly the frequency of financial transactions, creates market diversity of misinformed options.
http://harpub.tk/toxcredo.htm
Social challenge:
Attacks, threatens, bothers, and irritates. Continually
threatens people, their social, and familial bonds. Provides
a standard base of insults against which reactive behavior
can be monitored.
Maintains fear of
nature, thereby undermining people's support and alert
system.
3
Vaccines
Social challenge:
To attack, threaten, bother, and irritate. To continually
threaten people, social, and familial bonds.
To serve as a ritual
of obeisance, to dramatize germ theory, required for disinfo
campaign that protects industry.
Economic: Raises
social metabolism, thereby increases production, confusion,
dumbness, errors, disease, and the frequency of all interactions,
and importantly the frequency of financial transactions, creates market diversity of misinformed options.
http://harpub.tk/toxcredo.htm
4
Biased germ diagnostics
and pharma
Underlies and enables all the
above. Germ causation takes
precedence over industrial liability. Maintains fear of
nature, thereby undermining people's support and alert
system.
Toxicological
investigations are ignored, avoided, omitted, and punished.
Disseminating pesticide production data is illegal. Reporting of polio is
mandated. Fake studies are commonly submitted to EPA
(see "Toxic Deception" by Fagin, et al).
Germ studies, regardless of evidence, are awarded prizes, such as,
Nobel Laureate. Scientists commonly sign off on articles
ghost-written by chemical and pharma industries. Diagnoses for viral polio
only, were paid by
National Foundation for Infantile
Paralysis.
Dangerous
vaccines, biased diagnostics and pharma 'greed' all play
together, protecting industrial 'waste management' and simultaneously
opening the gates to medical exploitation. It is not necessary
to hire pharma to
exploit. They need only be allowed, through the corruption of
legislation and media, to take a piece of the action, to be
exploitive, to facilitate their legal protections. Everything
can appear free-market.
Vaccines and The Great Polio Epidemic
The
following selections are from
John Scudamore,
as he states vaccines were a factor in Britain, "
The following information by the
National Anti-Vivisection Society (UK) gives some insight into the
relationship between the diptheria and triple antigen vaccines and
paralytic polio."
"The early
triple vaccine against diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus had
also been shown beyond doubt to cause paralytic polio in some
children to whom it was administered. The incidence of polio in
children recently vaccinated against diphtheria was statistically
greater than in unvaccinated children, symptoms showing in the
vaccinated limb with 28 days of the initial injection. This scandal
broke in Britain during 1949, an epidemic year for polio, other
reports soon following from Australia. Papers dealing with this
topic are plentiful.
One, British, gives details of 17
cases of polio which followed 28 days or less after various
injections.
Another, Australian, gives details of
340 cases of polio, 211 of which had been previously vaccinated
against whooping cough and/or diphtheria. Of these, 35 had been
vaccinated within the preceding 3 months and a further 30 within the
previous year ( B.P. McClosky, "The Relation of Prophylactic
Inoculation to the Onset of Poliomyelitis," Lancet, April 18,
659-663. 1950?).
Dr Geffen reported similar findings
from the London borough of St Pancras, where 30 children under the
age of 5 developed polio within four weeks of being immunised
against diphtheria or whooping cough or both, the paralysis
affecting, in particular, the limb of injection. Two medical
statisticians at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
examined these reports and concluded that:
"Geffen (1950) noted in the 1949
epidemic 30 out of 182 paralytic patients under 5 had been immunised
against diptheria, pertussis, or both within weeks of contracting
polio. In all of these cases the limb last injected was paralysed;
in another seven cases a different limb was affected. In 21 of the
30 cases combined diptheria and pertussis vaccine had been used, APT
in eight, and pertussis alone in one. Geffen calculated that the
proportion of children becoming paralysed after immunisation was of
the order of 1 in 1800. The interval between injection and the
development of polio was usually between 5 and 16 days (Geffen,
Paterson and Tracy 1953)."--Wilson, The Hazards of Immunisation
Dr Arthur Gale of the Ministry of
Health reported 65 cases from the Midlands, where paralysis followed
about two weeks after an injection: in 49 of these, paralysis
occurred in the injected limb. Then it was reported that of 112
cases of paralysis admitted to the Park Hospital, London, during
1947-1949, 14 were paralysed in the limb which had received one or
more of a course of immunising injections within the previous two
months. In the majority of cases, the interval between the last
injection and the onset of paralysis was between 9 and 14 days.
Again, combined whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus injections
were involved.
This outbreak of polio followed an
intensive immunisation campaign during that time, 1947-49. Following
these findings, the Ministry of Health recommended that diphtheria
and triple vaccines should not be used in areas where polio was
naturally present. "From that time onwards, the incidence of
paralytic polio decreased rapidly in Britain, even prior to the
advent of Salk vaccination...."
|
Epidemic Factors Prioritized by Industrial Necessity |
||||
| Priority | Factor | Primary Effect | Secondary Effect | Tertiary Effect |
| 1 | Pollution (air, water, food) | Economic: Required means of free waste disposal. Must be protected from liabilities. | Requires masking by propaganda and disinfo. The effects of pollution are dark and would interfere with esprit de corp and tarnish the image of the current style of technology. | Economic: Raises social metabolism, thereby increases production, confusion, dumbness, errors, disease, and the frequency of all interactions, and importantly the frequency of financial transactions, creates market diversity of misinformed options. http://harpub.tk/toxcredo.htm |
| 2 | Pesticides | Economic: Raises social metabolism, thereby increases production, confusion, dumbness, errors, disease, and the frequency of all interactions, and importantly the frequency of financial transactions, creates market diversity of misinformed options. http://harpub.tk/toxcredo.htm | Social challenge: Attacks, threatens, bothers, and irritates. Continually threatens people, their social, and familial bonds. Provides a standard base of insults against which reactive behavior can be monitored. | Maintains fear of nature, thereby undermining people's support and alert system. |
| 3 | Vaccines | Social challenge: To attack, threaten, bother, and irritate. To continually threaten people, social, and familial bonds. | To serve as a ritual of obeisance, to dramatize germ theory, required for disinfo campaign that protects industry. | Economic: Raises social metabolism, thereby increases production, confusion, dumbness, errors, disease, and the frequency of all interactions, and importantly the frequency of financial transactions, creates market diversity of misinformed options. http://harpub.tk/toxcredo.htm |
| 4 | Biased germ diagnostics and pharma | Underlies and enables all the above. Germ causation takes precedence over industrial liability. Maintains fear of nature, thereby undermining people's support and alert system. | Toxicological investigations are ignored, avoided, omitted, and punished. Disseminating pesticide production data is illegal. Reporting of polio is mandated. Fake studies are commonly submitted to EPA (see "Toxic Deception" by Fagin, et al). | Germ studies, regardless of evidence, are awarded prizes, such as, Nobel Laureate. Scientists commonly sign off on articles ghost-written by chemical and pharma industries. Diagnoses for viral polio only, were paid by National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis. |
Dangerous vaccines, biased diagnostics and pharma 'greed' all play together, protecting industrial 'waste management' and simultaneously opening the gates to medical exploitation. It is not necessary to hire pharma to exploit. They need only be allowed, through the corruption of legislation and media, to take a piece of the action, to be exploitive, to facilitate their legal protections. Everything can appear free-market.
Vaccines and The Great Polio Epidemic
The following selections are from John Scudamore, as he states vaccines were a factor in Britain, "
The following information by the National Anti-Vivisection Society (UK) gives some insight into the relationship between the diptheria and triple antigen vaccines and paralytic polio."| "The early triple vaccine against diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus had also been shown beyond doubt to cause paralytic polio in some children to whom it was administered. The incidence of polio in children recently vaccinated against diphtheria was statistically greater than in unvaccinated children, symptoms showing in the vaccinated limb with 28 days of the initial injection. This scandal broke in Britain during 1949, an epidemic year for polio, other reports soon following from Australia. Papers dealing with this topic are plentiful. |
| One, British, gives details of 17 cases of polio which followed 28 days or less after various injections. |
| Another, Australian, gives details of 340 cases of polio, 211 of which had been previously vaccinated against whooping cough and/or diphtheria. Of these, 35 had been vaccinated within the preceding 3 months and a further 30 within the previous year ( B.P. McClosky, "The Relation of Prophylactic Inoculation to the Onset of Poliomyelitis," Lancet, April 18, 659-663. 1950?). |
| Dr Geffen reported similar findings from the London borough of St Pancras, where 30 children under the age of 5 developed polio within four weeks of being immunised against diphtheria or whooping cough or both, the paralysis affecting, in particular, the limb of injection. Two medical statisticians at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine examined these reports and concluded that: |
| "Geffen (1950) noted in the 1949 epidemic 30 out of 182 paralytic patients under 5 had been immunised against diptheria, pertussis, or both within weeks of contracting polio. In all of these cases the limb last injected was paralysed; in another seven cases a different limb was affected. In 21 of the 30 cases combined diptheria and pertussis vaccine had been used, APT in eight, and pertussis alone in one. Geffen calculated that the proportion of children becoming paralysed after immunisation was of the order of 1 in 1800. The interval between injection and the development of polio was usually between 5 and 16 days (Geffen, Paterson and Tracy 1953)."--Wilson, The Hazards of Immunisation |
|
Dr Arthur Gale of the Ministry of Health reported 65 cases from the Midlands, where paralysis followed about two weeks after an injection: in 49 of these, paralysis occurred in the injected limb. Then it was reported that of 112 cases of paralysis admitted to the Park Hospital, London, during 1947-1949, 14 were paralysed in the limb which had received one or more of a course of immunising injections within the previous two months. In the majority of cases, the interval between the last injection and the onset of paralysis was between 9 and 14 days. Again, combined whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus injections were involved. |
| This outbreak of polio followed an intensive immunisation campaign during that time, 1947-49. Following these findings, the Ministry of Health recommended that diphtheria and triple vaccines should not be used in areas where polio was naturally present. "From that time onwards, the incidence of paralytic polio decreased rapidly in Britain, even prior to the advent of Salk vaccination...." |
Industry's propaganda relation to people is mysterious. People, oddly, demand the blue pill.